На чтение 2 мин Просмотров 1.1к. Опубликовано 13.01.2021
Обновлено 13.01.2021
Доброго времени суток, дорогие читатели. Вы наверняка встречали записи или видеодорожки, в которых звук периодически замедлялся или ускорялся. На самом деле – это достаточно популярная практика, используемая как блоггерами, так и звукорями. И в сегодняшней статье мы расскажем вам, как добиться такого эффекта в Adobe Audition.
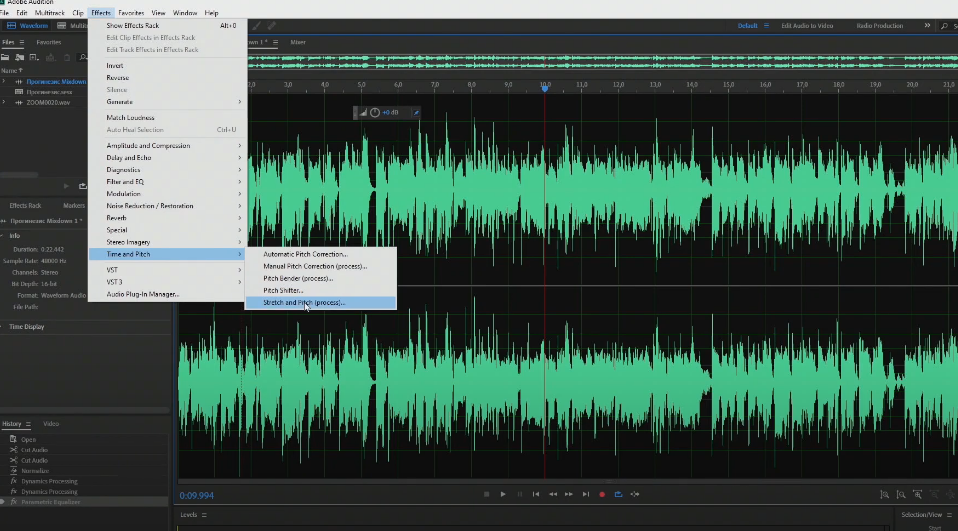
Итак, для того, чтобы перейти в эффекты настройки скорости звука, вам нужно будет выбрать, на верхней панели, вкладку «Effects». В открывшейся табличке выберите пункт «Time and Pitch», а в еще одной табличке выберите «Stretch and Pitch process».
После этого у вас откроется табличка, в которой и будут настройки скорости. Обратите внимание на ползунок внизу, где Stretch. 100% – Это нормальная скорость воспроизведения вашего звука.
Чем ниже будет значение – тем быстрее будет воспроизводиться запись. Соответственно, чем больше будет показатель на ползунке, тем медленнее звук будет воспроизводиться, т.е. вы получите тот самый эффект замедления голоса или записи в целом.
Собственно, вам всего-то и нужно будет, что выбрать нужное значение на ползунке, а после нажать на «Apply», дабы принять все изменения, а после экспортировать ваш файл в нужную папку на вашем компьютере.
На этом мы прощаемся с вами, всем удачи и до новых встреч.
( 1 оценка, среднее 5 из 5 )
Как изменить скорость воспроизведения звука
Необходимость поменять скорость воспроизведения звукового отрывка может возникнуть в разных ситуациях. Ускорять или замедлять звук приходится как при устранении рассинхронизации с видеорядом, так и при создании оригинальных треков. Выполнить эту задачу можно при помощи программы-аудиоредактора, в которой есть фильтры для работы со скоростью звукового фрагмента.

Вам понадобится
- — программа Adobe Audition;
- — звуковой файл.
Инструкция
Загрузите звук, с которым собираетесь работать, в Adobe Audition при помощи опции Open, Open Audio from Video, если вы редактируете звуковую дорожку видеофайла, или Extract Audio from CD, если вы открываете файл с компакт-диска.
Укажите фрагмент загруженного звука, скорость воспроизведения которого вы хотите изменить. Для этого поставьте указатель курсора в начало отрывка, зажмите левую кнопку мышки и выделите участок звуковой волны. Если вам нужно изменить весь файл, открытый в аудиоредакторе, можете ничего не выделять.
Для работы со скоростью воспроизведения звука в Adobe Audition вам потребуются фильтры, собранные в группе Time/Pitch из меню Effects. Если вам нужно замедлить или ускорить звук на известное количество процентов, сделайте это при помощи фильтра Stretch. Этот же фильтр позволяет подгонять продолжительность звучания под определенный отрезок времени. Окно его настроек открывается опцией Stretch (process).
Окно настроек фильтра по умолчанию открывается на вкладке Constant Stretch. Если вы собираетесь применить ко всему отрывку одинаковое изменение скорости, вам потребуется именно эта вкладка. В поле Stretch Mode в нижней части вкладки выберите режим изменения. В режиме Time Stretch вы сможете поменять скорость, сохранив тональность звука. Режим Resample меняет скорость и тональность.
Настройте изменение звука. Для этого вы можете указать новую длину файла в процентах, введя значение в поле Ratio. Исходный темп звука принимается за сто процентов. Если вам нужно ускорить звук, введите значение больше этой величины. Для замедления звука укажите величину меньше ста процентов.
В некоторых случаях, например, при исправлении рассинхронизации звука и видео, требуется растянуть или сократить звуковой фрагмент до определенной продолжительности. Это можно сделать, введя новую длительность звука в секундах в поле Length.
Если вам требуется по-разному изменить звук в начале и конце фрагмента, перейдите на вкладку Gliding Stretch и настройте коррекцию для разных частей файла. Начальная скорость настраивается в панели Initial, а состояние звука в конце редактируемого фрагмента определяется настройками в панели Final.
Прослушайте результат применения выставленных параметров, нажав на кнопку Preview. Отредактированный файл можно сохранить, использовав опции Save As или Save Copy As из меню File.
Источники:
- Помощь по организации работы с Adobe Audition
- как изменить звук на видео
Войти на сайт
или
Забыли пароль?
Еще не зарегистрированы?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Is it possible to the change the playback speed in Adobe Audition during editing and have it correct the pitch so only the tempo changes. For editing a podcast, I want to listen faster than real time without doing any destructive edits.
Just using J, K and L are ok but the higher pitch makes it difficult to listen to.
asked Jan 20, 2017 at 12:16
WilkaWilka
1911 gold badge1 silver badge5 bronze badges
1
Here’s a video that goes through how to speed it up without affecting the pitch.
Here are the steps:
- Enable Global Clip Stretching
- Select All tracks
- Drag the triangle on the top right of a track that will stretch and reduce to the speed you want.
- Once you’re done editing, remember to stretch it back to it’s normal speed.
answered Aug 30, 2017 at 12:45
this is the main reason I cut with a video editing too first (like screenflow). I use jkl all the time to navigate through a podcast episode… and I can’t find a reason why Adobe doens’t just implem
answered Aug 15, 2019 at 14:03
Is it possible to the change the playback speed in Adobe Audition during editing and have it correct the pitch so only the tempo changes. For editing a podcast, I want to listen faster than real time without doing any destructive edits.
Just using J, K and L are ok but the higher pitch makes it difficult to listen to.
asked Jan 20, 2017 at 12:16
WilkaWilka
1911 gold badge1 silver badge5 bronze badges
1
Here’s a video that goes through how to speed it up without affecting the pitch.
Here are the steps:
- Enable Global Clip Stretching
- Select All tracks
- Drag the triangle on the top right of a track that will stretch and reduce to the speed you want.
- Once you’re done editing, remember to stretch it back to it’s normal speed.
answered Aug 30, 2017 at 12:45
this is the main reason I cut with a video editing too first (like screenflow). I use jkl all the time to navigate through a podcast episode… and I can’t find a reason why Adobe doens’t just implem
answered Aug 15, 2019 at 14:03
- Audition User Guide
- Introduction
- What’s new in Adobe Audition
- Audition system requirements
- Finding and customizing shortcuts
- Applying effects in the Multitrack Editor
- Workspace and setup
- Control surface support
- Viewing, zooming, and navigating audio
- Customizing workspaces
- Connecting to audio hardware in Audition
- Customizing and saving application settings
- Digital audio fundamentals
- Understanding sound
- Digitizing audio
- Importing, recording, and playing
- Multichannel audio workflow
- Create, open, or import files in Adobe Audition
- Importing with the Files panel
- Extracting audio from CDs
- Supported import formats
- Navigate time and playing audio in Adobe Audition
- Recording audio
- Monitoring recording and playback levels
- Remove silences from your audio recordings
- Editing audio files
- Edit, repair, and improve audio using Essential Sound panel
- Generating text-to-speech
- Matching loudness across multiple audio files
- Displaying audio in the Waveform Editor
- Selecting audio
- How to copy, cut, paste, and delete audio in Audition
- Visually fading and changing amplitude
- Working with markers
- Inverting, reversing, and silencing audio
- How to automate common tasks in Audition
- Analyze phase, frequency, and amplitude with Audition
- Frequency Band Splitter
- Undo, redo, and history
- Converting sample types
- Creating podcasts using Audition
- Applying effects
- Enabling CEP extensions
- Effects controls
- Applying effects in the Waveform Editor
- Applying effects in the Multitrack Editor
- Adding third party plugins
- Notch Filter effect
- Fade and Gain Envelope effects (Waveform Editor only)
- Manual Pitch Correction effect (Waveform Editor only)
- Graphic Phase Shifter effect
- Doppler Shifter effect (Waveform Editor only)
- Effects reference
- Apply amplitude and compression effects to audio
- Delay and echo effects
- Diagnostics effects (Waveform Editor only) for Audition
- Filter and equalizer effects
- Modulation effects
- Reduce noise and restore audio
- Reverb effects
- How to use special effects with Audition
- Stereo imagery effects
- Time and pitch manipulation effects
- Generate tones and noise
- Mixing multitrack sessions
- Creating remix
- Multitrack Editor overview
- Basic multitrack controls
- Multitrack routing and EQ controls
- Arrange and edit multitrack clips with Audition
- Looping clips
- How to match, fade, and mix clip volume with Audition
- Automating mixes with envelopes
- Multitrack clip stretching
- Video and surround sound
- Working with video applications
- Importing video and working with video clips
- 5.1 surround sound
- Keyboard shortcuts
- Finding and customizing shortcuts
- Default keyboard shortcuts
- Saving and exporting
- Save and export audio files
- Viewing and editing XMP metadata
Automatic Pitch Correction effect
The Automatic Pitch Correction effect is available in both the Waveform and Multitrack editors. In the latter, its parameters can be automated over time using keyframes and external control surfaces.
Choose Effects > Time and Pitch > Automatic Pitch Correction, and set the following options:
Scale
Specifies the scale type that best suits the material: Major, Minor, or Chromatic. Major or Minor correct notes to the specific key of the music. Chromatic corrects to the nearest note regardless of key.
Key
Sets the intended key for corrected material. This option is available only if Scale is set to Major or Minor (because the Chromatic scale includes all 12 tones and isn’t key‑specific).
The combination of scale and key determines the key signature.
Attack
Controls how quickly Adobe Audition corrects the pitch toward the scale tone. Faster settings are usually best for notes of short duration, such as a fast, staccato passage. An extremely fast attack can achieve a robotic quality, however. Slower settings result in more natural‑sounding correction on longer sustaining notes, such as a vocal line where the singer holds notes and adds vibrato. Because source material can change throughout a musical performance, you can get the best results by separately correcting short musical phrases.
Sensitivity
Defines the threshold beyond which notes aren’t corrected. Sensitivity is measured in cents, and there are 100 cents per semitone. For example, a Sensitivity value of 50 cents means a note must be within 50 cents (half a semitone) of the target scale tone before it is corrected automatically.
Reference Channel
Choose a source channel in which pitch changes are most clear. The effect analyzes only the channel you choose, but applies the pitch correction equally to all channels.
FFT Size
Sets the Fast Fourier Transform size of each pieces of data that the effect processes. In general, use smaller values for correcting higher frequencies. For voices, a setting of 2048 or 4096 sounds most natural. For short, staccato notes or percussive audio try a setting of 1024.
Calibration
Specifies the tuning standard for the source audio. In Western music, the standard is A4 at 440 Hz. Source audio, however, may have been recorded using a different standard, so you can specify A4 values from 410 to 470 Hz.
Correction meter
When you preview audio, displays the amount of correction for flat and sharp tones.
Manual Pitch Correction effect
The Manual Pitch Correction effect lets you visually adjust pitch with the Spectral Pitch Display. The Spectral Pitch Display shows the fundamental pitch as a bright blue line, and overtones in yellow to red hues. Corrected pitch appears as a bright green line.
You can visually monitor pitch at any time, without using the Manual Pitch Correction effect. Simply click the Spectral Pitch Display icon in the options bar. To customize resolution, decibel range, and gridlines, adjust Pitch Display settings in the Spectral Displays preferences.
-
Choose Effects > Time and Pitch > Manual Pitch Correction.
-
In the Manual Pitch Correction window, set the following options:
Reference Channel
Choose a source channel in which pitch changes are most clear. The effect analyzes only the channel you choose, but applies the pitch correction equally to all channels.
Spline Curves
Create smoother transitions when using envelope keyframes to apply different pitch correction over time.
Pitch Curve Resolution
Sets the Fast Fourier Transform size of each piece of data that the effect processes. In general, use smaller values for correcting higher frequencies. For voices, a setting of 2048 or 4096 sounds most natural, and a setting of 1024 creates robotic effects.
-
In the Editor panel, do either of the following:
- To change pitch uniformly, drag the Adjust Pitch knob in the heads-up display.
- To change pitch over time, add keyframes to the yellow envelope line in the center of the waveform display.
To zoom in on specific pitch ranges, right-click and drag in the vertical ruler to the right of the Spectral Pitch Display. To reset the zoom level or customize the displayed scale, right-click the ruler and select options from the pop-up menu.
Pitch bender effect
Use the Pitch Bender effect to change the tempo over time to vary the pitch. The effect now uses a keyframe edit envelope laid across the entire waveform, similar to the Fade and Gain Envelope effects.
Choose Effects > Time and Pitch > Pitch Bender, and set the following options:
Pitch
In the Editor panel, click the blue envelope line to add keyframes, and drag them up or down to change amplitude. To quickly select, reposition, or delete multiple keyframes, see Adjust automation with keyframes.
Select the Spline Curves option to create smoother, curved transitions between keyframes, rather than linear transitions. See About spline curves for graphs.
Quality
Controls the quality level. Higher quality levels produce the best sound, but they take longer to process. Lower quality levels produce more unwanted harmonic distortion, but they take less time to process. Usually, you won’t notice harmonic distortion for levels from Very Good and higher. Aliasing still occurs, however, when you shift the pitch up, but the higher quality levels greatly reduce the distortion when you shift the pitch down.
Range
Sets the scale of the vertical ruler (y-axis) as semitones (there are 12 semitones to an octave) or as beats per minute. For a range in semitones, the pitch changes logarithmically, and you can specify the number of semitones to shift up or down. For a range in beats per minute, the pitch changes linearly, and you must specify both a range and a base tempo. You can specify the exact tempo of a selection to change to different rates, but this isn’t required.
Pitch shifter
The Pitch Shifter effect changes the musical pitch. It’s a real-time effect which can be combined with other effects in the mastering rack or the effects rack. In the Multitrack View, you can also vary pitch over time by using automation lanes.
Choose Effects > Time and Pitch > Pitch Shifter effect, and set the following options:
Pitch Transpose
Contains options that adjust pitch:
- Semi-Tones Transposes pitch in semi-tone increments, which equalmusical half-notes (for example, the note C# is one semi-tone higher than C). A setting of 0 reflects the original pitch; +12 semi-tones is an octave higher; -12 semi-tones is an octave lower.
- Cents Adjusts pitch in fractions of semi-tones. Possible values range from -100 (one semi-tone lower) to +100 (one semi-tone higher).
- Ratio Determines the relationship between shifted and original frequency. Possible values range from 0.5 (an octave lower) to 2.0 (an octave higher).
Precision
Determines sound quality, with theHigh setting taking longest to process. Use the Low setting for 8-bit or low-quality audio, and use the High setting for professionally recorded audio.
To quickly determine which Precision setting to use, process a small selected range at each setting until you find the best balance of quality and processing time.
Pitch Settings
Control how audio is processed:
- Splicing Frequency Determines the size of each chunk of audio data. (The Pitch Shifter effect divides audio into very small chunks for processing.) The higher the value, the more precise the placement of stretched audio over time. However, artifacts become more noticeable as values go up. At higher Precision settings, a lower Splicing Frequency may add stutter or echo. If the frequency is too high, sound becomes tinny and voices have a tunnel-like quality.
- Overlapping Determines how much each chunk of audio data overlaps with the previous and next ones. If stretching produces a chorus effect, lower the Overlapping percentage. If doing so produces a choppy sound, adjust the percentage to strike a balance between choppiness and chorusing. Values range from 0 to 50%.
- Use Appropriate Default Settings Applies good default values for Splicing Frequency and Overlapping.
Stretch and Pitch effect (Waveform
Editor only)
The Time And Pitch > Stretch And
Pitch effect lets you change the pitch of an audio signal, the tempo,
or both. For example, you can use the effect to transpose a song
to a higher key without changing the tempo, or you can use it to
slow down a spoken passage without changing the pitch.
This effect requires offline processing. While it is open,
you cannot edit the waveform, adjust selections, or move the current-time
indicator.
Algorithm
Choose IZotope Radius to simultaneously stretch audio and
shift pitch, or Audition to change stretch or pitch settings over
time. The iZotope Radius algorithm requires longer processing but
introduces fewer artifacts.
Precision
Higher settings produce better quality but require more processing time.
New Duration
Indicates how long the audio will be after time-stretching. You can either adjust the New Duration value directly, or indirectly by changing the Stretch percentage.
If you commonly stretch files to a certain duration, click the Favorite icon to save that setting for future use. To apply a favorite to multiple files, see Batch process files.
Lock Stretch Settings to New Duration
Overrides custom or preset Stretch settings, instead calculating them from duration adjustments.
Select the option above to quickly make radio spots 30 or 60 seconds long.
Stretch
Shortens or extends processed audio relative to existing
audio. For example, to shrink audio to half its current duration,
specify a Stretch value of 50%.
Pitch Shift
Tonally shifts audio up or down. Each semitone equals one
half‑step on a keyboard.
Final Stretch or Pitch Shift (Audition algorithm)
Changes the initial Stretch or Pitch Shift setting over time,
reaching the final setting at the last selected audio sample.
Lock Stretch and Pitch Shift (IZotope algorithm)
Stretches audio to reflect pitch changes, or vice versa.
Lock Initial Strech and Pitch Shift (Audition algorithm)
Stretches audio to reflect pitch changes, or vice versa.
Final Stretch or Pitch Shift settings are unaffected.
Advanced settings (IZotope Radius algorithm)
Click the triangle to access these options:
Solo Instrument Or Voice
More quickly processes a solo performance.
Preserve Speech Characteristics
Maintains realism in speech.
Formant Shift
Determines how formants adjust to pitch shifts. The default value
of zero adjusts formants together with pitch shifts, maintaining
timbre and realism. Values above zero produce higher timbres (making
a male voice sound female, for example). Values below zero do the
reverse.
Pitch Coherence
Maintains timbre of solo instruments or vocals. Higher values reduce
phasing artifacts but introduce more pitch modulation.
Advanced settings (Audition algorithm)
Click the triangle to access these options:
Splicing Frequency
Determines how big each chunk of audio data is when you preserve
pitch or tempo while stretching a waveform. The higher the value,
the more precise the placement of stretched audio over time. However,
artifacts are more noticeable as rates go up; sound can become tinny
or have a tunnel‑like quality. With higher Precision settings, lower
splicing frequencies may add stutter or echo.
Overlapping
Determines how much each chunk of audio data overlaps with the
previous and next ones. If stretching produces a chorus effect,
lower the Overlapping percentage, without going so low that you
produce a choppy sound. Overlapping can be as high as 400%, but
you should use this value only for very high speed increases (200%
or more).
Choose Appropriate Defaults
Applies good default values for Splicing Frequency and Overlapping.
This option is good for preserving pitch or tempo.
Constant Vowels
Preserves the sound of vowels in stretched vocals. This option requires
substantial processing; try it on a small selection before applying
it to a larger one.
Adobe Employee
,
Jul 13, 2013
Jul 13, 2013
_durin_
•
Adobe Employee
,
Jul 13, 2013
Jul 13, 2013
There are a few ways to slow a portion of a track down. Use Effects > Time & Pitch > Stretch and PItch (process). If you choose the Audition algorithm, you can perform a gliding stretch which will let you stretch from 100% (normal playback) up to 800% (8x slower) over time.
If you’re using Audition CC, the Pitch Bender effect will allow you to keyframe the slowdown on screen so you can draw the curve and duration you want directly on the waveform.
Adobe Employee
,
Jul 13, 2013
Jul 13, 2013
_durin_
•
Adobe Employee
,
Jul 13, 2013
Jul 13, 2013
There are a few ways to slow a portion of a track down. Use Effects > Time & Pitch > Stretch and PItch (process). If you choose the Audition algorithm, you can perform a gliding stretch which will let you stretch from 100% (normal playback) up to 800% (8x slower) over time.
If you’re using Audition CC, the Pitch Bender effect will allow you to keyframe the slowdown on screen so you can draw the curve and duration you want directly on the waveform.
Time Stretch — полезная функция, с помощью которой можно изменить длину и «темп» выбранного фрагмента аудиоданных, при этом не затрагивая высоту тона. Рассмотрим в этой статье особенности применения этой функции и покажем несколько примеров.
Содержание
- Time Stretch (растяжка по времени)
- Что из себя представляет функция Time Stretch?
- Варианты применения функции Time Stretch
- Time Stretch в Cubase, Nuendo
- СекцияDefine Bars (определения тактов)
- СекцияOriginal Length (Исходная длительность)
- Секция ResultingLength(Результирующая длительность)
- СекцияSeconds Range (Диапазон в секундах)
- СекцияTime Stretch Ratio (Коэффициент Time Stretch)
- СекцияAlgorithm (алгоритм)
- Time Stretch в Reaper
- Time Stretch в Samplitude
- Секция Algorithm
- Time Stretch FL Studio
- Секция Amount
- Time Stretch в Adobe Audition
- Constant Stretch
- Группа Pitch and Time settings
- Gliding Stretch
- Группа Pitch and Time settings
- Общие параметры для вкладок Constant Stretch иGliding Stretch
Time Stretch (растяжка по времени)
Функция растяжения аудиофайла по времени имеется практически во всех программах цифровой обработки музыки. Конечно, в каждой из них функция Time Stretch может называться немного по другому, например: Cubase, Nuendo (Time Stretch); Reaper (time stretch); FL Studio (Time Stretch); Samplitude (Time Stretching); Audition (Stretch) и т. д., но в целом найти её не составит проблем.
Что из себя представляет функция Time Stretch?
Данная функция Stretch (растяжение) построена на предварительном разбиении звукового фрагмента на элементы (выборки). Впоследствии каждая из выборок при необходимости обрабатывается отдельно, а затем опять собирается в результирующий сигнал. Длительность воспроизведения волновой формы при этом увеличивается (уменьшается), а высота тона не изменяется.
Варианты применения функции Time Stretch
Обычно возможно два варианта применения этой функции: быстрый и точный.
Быстрый вариант реализуется так:
- В быстром меню инструментов выбирается функция Time Stretch (ниже примеры из программы Samplitude, Cubase, Nuendo)
- Затем нужно навести курсор мыши на окончание одного из аудиофайлов. Вид курсора при этом может изменится на изображении руки, часов и т. п.
- Захватите конец файла и перетащите мышь влево (чтобы увеличить скорость воспроизведения) или вправо (чтобы замедлить его).
Этот вариант действительно быстрый и может применяться когда файл не нуждается в точной подстройки под темп проекта (например, эффект, шум и т. п.)
Для точной настройки и «подгона» под нужный темп имеется второй вариант.
Точный вариант
Для этого нужно:
- Выберите нужный аудиофайл.
- Вызвать в меню функцию Time Stretch .
- Откроется диалоговое окно с различными параметрами: продолжительность файла, темп, алгоритм преобразования и т. д.
- Внесите изменения и нажмите OK.
Теперь перейдём к конкретным примерам.
Time Stretch в Cubase, Nuendo
Меню Time Stretch открывается командой Audio > Process > Time Stretch
Доступны следующие параметры:
Секция Define Bars (определения тактов)
Если вы используете настройки темпа, вы можете задать длину выбранного аудио и размер в этой секции.
- Bars (Такты) — Устанавливает длину выбранного аудио в тактах.
- Beats (Доли) — Устанавливает длину выбранного аудио в долях.
- Sign. (Размер) — Задаёт размер.
Секция Original Length (Исходная длительность)
Эта секция содержит информацию и настройки, касающиеся выбранного для обработки аудио.
- Length in Samples (Длина в семплах) — Длина выбранного аудио в семплах.
- Length in Seconds (Длина в секундах) — Длина выбранного аудио в секундах.
- Tempo in BPM (Темп в BPM (уд/мин) — Позволяет вам ввести действительный темп аудио в ударах в минуту. Эта опция позволяет вам производить пересчёт аудио в другой темп, без расчёта необходимых коэффициентов растяжения или сжатия.
Секция Resulting Length (Результирующая длительность)
Это значение изменяется автоматически при регулировке Коэффициента Time Stretch для растяжения (сжатия) аудио, чтобы оно было привязано к определённому временному интервалу или темпу.
- Samples (Семплы) — Результирующая длина в семплах.
- Seconds (Секунды) — Результирующая длительность в секундах.
- BPM — Результирующий темп в ударах в минуту. Для этого необходима установка параметра Исходная длительность.
Секция Seconds Range (Диапазон в секундах)
Позволяет вам задать диапазон для растяжения по времени.
- Первая строчка — Произвольное время вступления. Позволяет вам задать начальную позицию диапазона.
- Вторая строчка — Позволяет вам задать конечную позицию диапазона.
- Use Locators (Использовать локаторы) — Позволяет вам установить значения Диапазона для левого и правого локаторов соответственно.
Секция Time Stretch Ratio (Коэффициент Time Stretch)
Определяет степень растяжения или сжатия в процентах от оригинальной длины. Если вы используете настройки в секции Результирующая длительность для установки степени растяжения, это значение изменяется автоматически.
Секция Algorithm (алгоритм)
Позволяет вам выбрать алгоритм растяжения по времени. Алгоритм MPEX — обрабатывает материал менее быстро, но с более высоким качеством. Realtime — наоборот, более быстро, но с худшим качеством.
Time Stretch в Reaper
Секции Take properties и Take pitch shift/time stretch mode окна Item Properties (F2) могут использоваться для растяжения клипа по времени.
Для этого необходимо отредактировать параметр Playback Rate. На рисунке ниже, скорость воспроизведения увеличена на 2%, и отмечена опция Preserve Pitch. В качестве алгоритма выбран Elastique 3 Pro.
Чтобы открыть окно Item Properties любого клипа, выберите клип и нажмите клавишу F2. Чтобы сделать это для нескольких клипов:
- Выберите нужные клипы.
- Нажмите клавишу F2.
- Диалоговое окно Item Properties включает параметры, изменения которых затронут несколько клипов сразу, включая параметры изменения высоты тона, и настройка скорости воспроизведения.
- Внесите изменения и нажмите OK.
Когда окно Item Properties открывается для нескольких клипов, некоторые опции будут затенены и, следовательно, не доступны. (например, опции Take envelopes и Rename file). Однако большинство опций доступно.
Time Stretch в Samplitude
В этой программе имеется плагин Resampling / Time Stretching. Он преобразует частоту дискретизации, растягивает/сжимает звук во времени, изменяет высоту тона. Открывается командой Effects > Time /Pitch > Resampling / Time Stretching главного меню программы.
Плагин не применяется в реальном времени. Однако кнопкой Play / Stop можно включить режим предварительного прослушивания обработанного материала, а кнопкой Play Original — материала исходного.
Интерфейс плагина предельно прост. Окно разделено на три секции. В секции Factor находятся два регулятора, управляющие параметрами преобразования:
- Time factor — относительный коэффициент сжатия/растяжения аудиоматериала во времени;
- Pitch (Half steps) — интервал транспонирования в полутонах.
В секции Time Factor Calculation расположены взаимосвязанные поля калькулятора, позволяющего пересчитать изменение длительности аудиоматериала в обрабатываемом объекте в изменение темпа и наоборот. Кнопка Reset приводит регуляторы и содержимое полей ввода в нейтральное положение, а обрабатываемый материал — в исходное.
Секция Algorithm
В раскрывающемся списке нужно выбрать алгоритм преобразования (один из восьми), в наибольшей степени соответствующий характеру обрабатываемого материала. Для удобства пользователя, если выделить в этом списке любую строку, автоматически откроется связанное с этой строкой окно, где в виде таблицы представлены сведения о том, в какой степени данный алгоритм пригоден для обработки того или иного аудиоматериала (барабанных партий, партий полифонических и одноголосных инструментов, вокала и т. д.).
Если установлен флажок Anti Aliasing Filter (High Quality Resampling), то преобразования будут выполнены с применением фильтра, предотвращающего искажения, вызванные наложением спектра дискретизированного сигнала на спектр сигнала исходного (эффект алиасинга).
Time Stretch FL Studio
Чтобы открыть инструмент Time Stretch / Pitch Shift нужно щелкнуть левой кнопкой мыши на кнопке Time Tool, нажать (Alt + T) внутри Редактора, либо использовать Tools > Time > Time stretch / Pitch. Чтобы открыть диалоговое окно «Вставить-растянуть», нажмите (Ctrl + Shift + T) или используйте Tools > Edit > Paste.
Секция Amount
- Pitch coarse — Грубая высота тона. Изменение основного тона в полутонах.
- fine — базовый шаг в центах
- mui — множитель диапазона высоты звука (в%)
- Time mul — изменить продолжительность выборки в%
- length — измените длительность выборки, указав длину в миллисекундах (мс)
- Method — выберите один из следующих методов смещения / сохранения высоты тона
- Insert — если этот переключатель выключен образец будет смешиваться с оригиналом.
Следующая секция Formant preservation изменяет параметры pitch высоты тона, поэтому мы их рассмотрим в другой статье.
Time Stretch в Adobe Audition
Для запуска выберите команду Effects > Time and Pitch > Strech
Имеется две основные вкладки: Constant Stretch и Gliding Stretch
- Constant Stretch (постоянное), то есть растяжение аудиофайла выполняется целиком без изменения стечением времени с одним и тем же коэффициентом.
- Gliding Stretch (изменяющееся) можно выбрать величину растяжения для исходной и конечной волн по отдельности.
Рассмотрим подробнее каждую из вкладок.
Constant Stretch
Ползунок Stretch % — предназначен для задания величины, на которую изменится время воспроизведения волновой формы (волна может быть расширена или сжата). Перемещение этого ползунка влияет на изменения параметров Ratio и Length. При сжатие (менее 100%) или растяжении (более 100%) волны отображается — Compress Wave и Stretch Wave. В положении 100% ширина волны не изменится (Unchancged).
Поле Ratio — отношение времени воспроизведения к высоте тона волновой формы (в процентах)
Поле Length — конечное время изменения ширины волны
При изменение любого из трёх параметров изменяются все остальные.
В окне Transpose выбирается количество полутонов для понижения или повышения аудиофрагмента.
Группа Pitch and Time settings
Флажок Solo Instrument or Voice позволяет более аккуратно выполнить настройку сольной партии. Флажок Preserve Speech Characteristics позволяет сохраеить реалистичность звуков речи. Поле Formant Shift Semitones касаются формантной настройки сдвига тона.
Gliding Stretch
В этой вкладке появляется два ползунка Initial %, Final % (первоначальный %, финальный %). Остальные параметры (Ratio, Length,Transpose) такие же как и в Constant Stretch.
Группа Pitch and Time settings
В этом режиме в данной группе появляются следующие параметры:
Поле Splicing Freguency. В этом поле указывается частота сращивания (5-500 Гц), определяющая количество выборок, на которые делится звуковой фрагмент. Значение этого параметра должно быть в целое число раз меньше частоты синусоидального колебания (частоты тонального заполнения), из которого состоит преобразуемая волновая форма.
Поле Overlapping. Предназначено для задания значения (0-50%) степени перекрытия звуковых выборок. При растяжении или сжатии выборки перекрываются друг другом.
Общие параметры для вкладок Constant Stretch и Gliding Stretch
Группа Precision имеет три варианта:
- Low Precision (низкая точность);
- Medium Precision (средняя точность);
- High Precision (высокая точность).
Группа Stretching Mode также имеет три переключателя:
- Time Stretch (Preserves Pitch) — позволяет уменьшать и увеличивать темп без изменения высоты тона;
- Pitch Shift (Preserves Tempo) — позволяет уменьшать и увеличивать высоту тона (питч) без изменения темпа;
- Resample (Preserves Neither) — позволяет изменять как высоту, так и темп.
В группе Presets содержится несколько готовых вариантов настроек:
- Culting Power. Постепенное растяжение выделенного фрагмента. Если обрабатывать однотонный звук, то получается эффект звука выстрела и полёта снаряда.
- Double Speed. Двухкратное сжатие во времени с одновременным повышением тона.
- Fast Talker и Speed up. Увеличение темпа или сжатие фрагмента волновой формы с сохранением высоты тона.
- Helium и Raisw Pitch. Повышение высоты звучания выделенной волновой формы при её неизменной длительности.
- Slow Down. Растяжение фрагмента волновой формы во времени в полтора раза с сохранением прежней высоты тона.
Всем спасибо и удачи в творчестве!
Подписывайтесь на RSS блога и следите за новыми статьями.
[DISPLAY_ULTIMATE_SOCIAL_ICONS]